Elevate Your Medical Education
On-demand education solutions for Doctors and Health Professionals

Years of experience in the medical field

Expert Instructors so you can learn with confidence

Unlimited access. Choose your schedule
Explore Our Most Popular Courses
Our courses are meticulously designed to meet the unique needs of medical professionals like you. Whether you're a doctor seeking to enhance your clinical skills, a clinician looking to stay updated with the latest advancements, or a healthcare provider aiming to deliver exceptional patient care, Meducate is your gateway to continuous professional growth
Unlock the Power of Knowledge. Start Your Journey with Meducate Today.
Join Us On Our Shows
Welcome to MedHeads, your go-to destination for insightful discussions on today's issues through a biopsychosocial lens. Join Dr. Ferghal Armstrong and a team of experts as they explore addiction medicine on Cracking Addiction. From science to treatment options, dive deep into the world of addiction every week. Tune in for evidence-based insights and guest perspectives. Break the cycle of addiction with us.
Igniting Academic Excellence
Click below to access talks and training, completely free.

Build Relevant Skills
Start building your skillset now to achieve your dream of becoming a specialist. Our courses provide the opportunity to enhance your expertise, helping you attain your professional goals.

Take Charge Of Your
Career
Our on-demand training provides a convenient solution for busy healthcare. Take the initiative to advance your career at your own pace and schedule, without compromising your busy schedule.
Remain Informed
Our courses provide guidance for health professionals in making informed decisions aligned with their expertise and passion, assisting with career direction when uncertain.
Take Action
Every training is designed to help you succeed. You're not just learning from a book. We give you guidelines for taking action and applying what you learn right away.

Learn From The Professionals
Our team is highly qualified to deliver you actionable knowledge that will help catapult your career into something that you've always dreamed of.
Learn Anytime,
Anywhere
Access our virtual portal to enhance your professional development through a flexible, on-demand system. Learn at your convenience and empower your growth with ease.
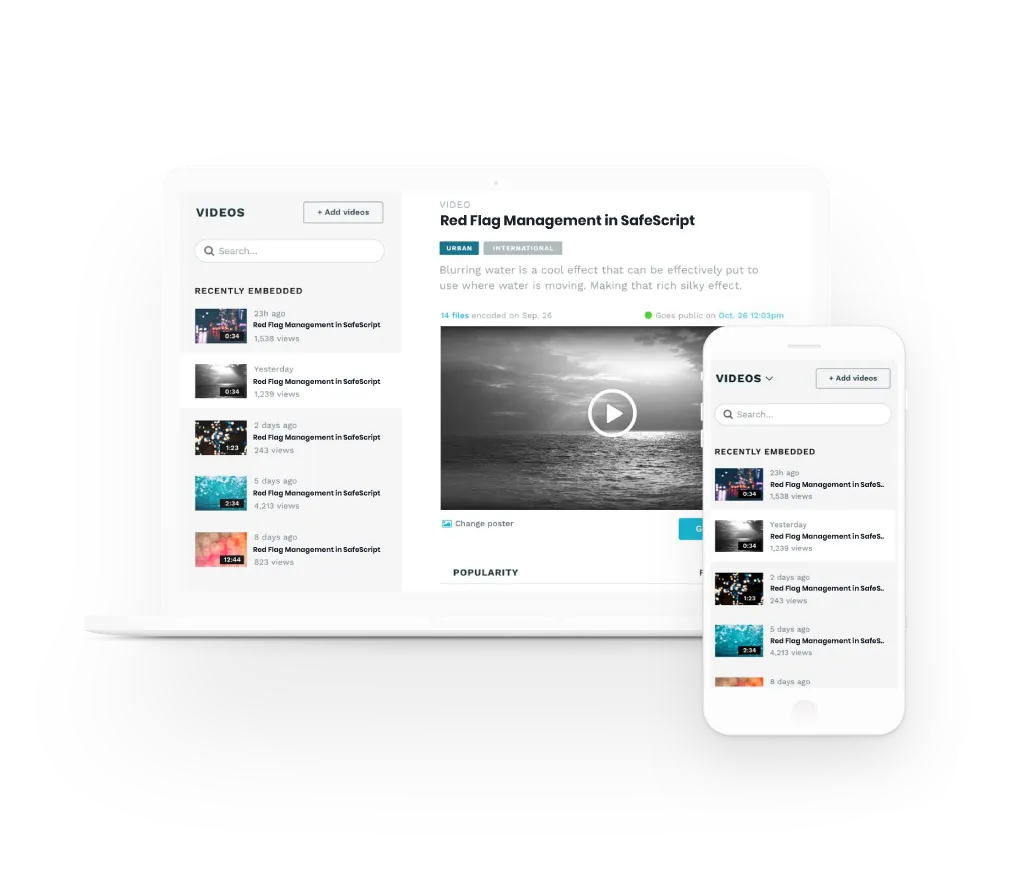
Benefits of Meducate Courses
Access all online courses
Membership previledges
Private Members Only Forum
Gamify your learning and boost knowledge
Cross device friendly
Quizzes & Assessments

About Meducate ®
Meducate® offers online education tailored to the specific needs of medical professionals, including doctors, clinicians, and other healthcare providers. Our team of educators and founders bring together expertise in medical education and digital media to develop customised training programs that go beyond conventional expectations.
We recognise that one of the biggest challenges in medical education is the lack of easily accessible and relevant training. To address this issue, Meducate was established to provide comprehensive and ongoing courses that can be accessed from anywhere, eliminating the need for attending weekend seminars or traveling long distances.
Our commitment to medical education is demonstrated through the continuous development of new courses, which are designed to meet the ever-changing needs of the healthcare industry. By subscribing to Meducate, you will be the first to know about our latest offerings, including brand-new classes, free on-demand training, and podcasts, which are all aimed at helping you achieve your professional goals.
Our Team
Dr. Ferghal Armstrong is a highly qualified medical professional with extensive experience in addiction medicine and various other medical specializations. He has been practicing medicine since 2003 and holds qualifications in addiction medicine, dermatology, skin cancer treatment, occupational medicine, obstetrics and gynecology, and pediatrics. He is a FAChAM Fellow and MATOD trainer, committed to providing high-quality medical care.

Dr. Ferghal Armstrong
Co Founder & CEO
Tony has over 35 years of experience in media production and collaborates with medical experts to create top-tier training videos for Meducate. These videos offer practical and comprehensive training for medical professionals, keeping them up-to-date with the latest techniques. Tony's commitment to producing high-quality content ensures that Meducate's videos are informative and engaging, helping professionals enhance their skills.

Tony Laughton
Co Founder and CTO
Jacqui holds a Masters in Business Administration; Masters in Dementia Care and Diploma's in Working with Vulnerable Adults and General Practice Management. She has extensive experience and expertise in managing aged care residential services; providing adult education for the Alzheimer's Society and Prison Services and conducting investigations in adult abuse allegations.

Jacqui Coombes
Business Manager & Dementia Care Specialist
Meducate® is a registered trademark in Australia
© ® Meducate 2024





